What is a standard cost?

The procedure is also repeated with output to ensure that production is equal to the standard. Standards are essential in every business entity to curtail high costs and ensure that output is maximized. The continuous budget is revised each month to add a new month to replace the one that has just been completed. This is a time-consuming approach, but does allow for incremental changes to the budget.
- Our goal is to deliver the most understandable and comprehensive explanations of financial topics using simple writing complemented by helpful graphics and animation videos.
- After necessary calculations, if the variance between the standard and the actual cost is positive, the company made progress.
- The actual costs incurred during production or service delivery are then compared to the predetermined costs, and any differences are tracked as variances.
- In short, the standard budget is the traditional method for deriving a budget, but it is severely limited, and if followed too rigorously, does not allow a business to take advantage of new opportunities on short notice.
- Standards and budgets are mutually exclusive which means standards can be set without the need to prepare an extensive budget and budgets can be prepared without the need for detailed standard costing.
- On the other hand, if the variance is negative, the company will likely run at a loss or deficit.
Ask a Financial Professional Any Question
If a company wants to be able to create budgets, forecast cash flows, or keep expenses consistent, it needs these numbers. Explain these types of costing methods to your clients and let them know which ones they should track and use. Here, budget refers to a written financial statement expressed in monetary terms prepared in advance for future periods, containing the details about the economic activities of the business organization. While a budget refers to a forecasted list of future income and expenditures, a standard is a benchmark that determines what cost the company cannot exceed and what amount of output is considered fundamental. After necessary calculations, if the variance between the standard and the actual cost is positive, the company made progress.
Using all These Different Costs Together
For example, if a client is trying to create a budget and knows prices are going up, it can add the projected increase in materials to the standard price to create the budgeted amount. This actually means that any fixed expenses are not altered in the budget, while expenses considered to be variable will adjust in the budget, based on the actual sales generated within a budget period. The budget model may also contain some mixed costs, which contain a fixed element and a variable element; in this case, only the variable element is altered in accordance with sales levels. While standard costs can be a useful management tool for a manufacturer, the manufacturer’s external financial statements must comply with the cost principle and the matching principle. Therefore, significant variances must be reviewed and properly assigned or allocated to the cost of goods sold and/or inventories.
How confident are you in your long term financial plan?
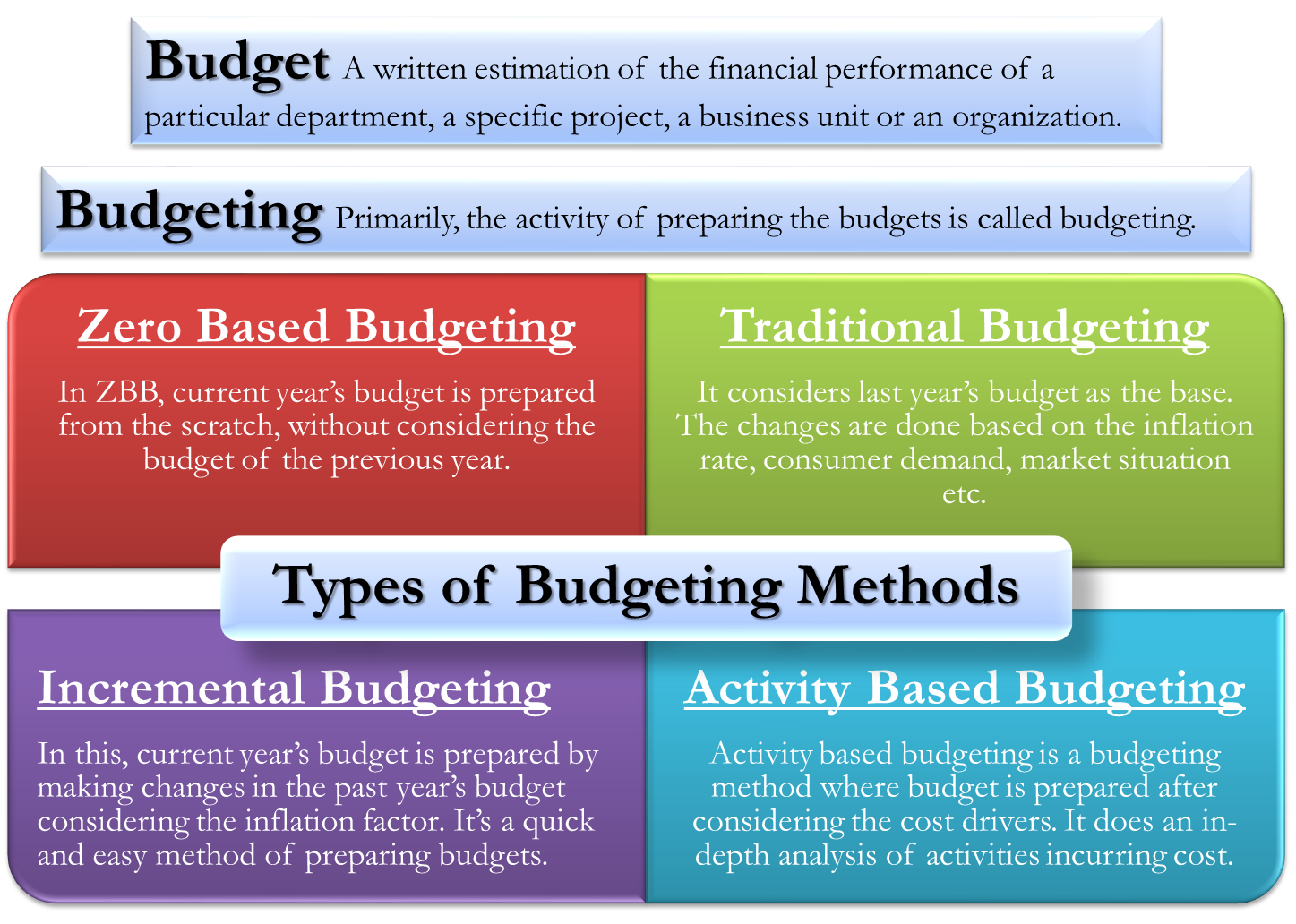
Setting of standards and budgets have the common intention of achieving cost management and cost control. Standards and budgets are mutually exclusive which means standards can be set without the need to prepare an extensive budget and budgets can be prepared without the need for detailed standard costing. For example, in a manufacturing entity, a standard will be set for the per unit direct materials cost, per unit direct labor cost and per unit overhead cost for each individual product the entity manufactures. A budget is a statement of estimated incomes and expenses over a specific time period. It can be prepared for a single project or a department or for an entity as a whole.
If it sees that difference immediately, it knows its profits are likely to be higher than usual. Similarly, if a company uses $20,000 as a standard figure for monthly labour expenses but then incurs $25,000 in payroll costs, the accounting records immediately note that 25% increase. Budgeted costs tend to overlap with standard costs, but they’re not exactly the same. In many cases, companies take the standard costs from the previous year and use them as their budgeted costs for the current year. Alternatively, businesses can use standard costs as a jumping off point to set their budgeted costs. In many situations, companies break down standard costs per unit, but they use budgeted costs for overall expenses.
Conclusion – standards vs budgets
This team of experts helps Finance Strategists maintain the highest level of accuracy and professionalism possible. Our team of reviewers are established professionals with decades of experience in areas of personal finance and hold many advanced degrees and certifications. 11 Financial may only transact business in those states in which it is registered, or qualifies for an exemption or exclusion from registration requirements.
It does not provide for any variability in the amount of units sold, price points, activity levels, and so forth. As such, a standard budget represents a single best estimate of the future performance of a business through the budgeting period. This approach works best when the business model is relatively simple, revenues rarely deviate from expectations, and expenses are highly predictable. Conversely, it functions poorly in a more fluid business environment that is more difficult to predict. The standard budget is commonly used in a centralized command-and-control environment, since it allows senior management to judge the performance of the organization in comparison to a single forecast of future results.
A budget generally refers to a department’s or a company’s probable revenues, costs, or expenses. A standard generally refers to a projected amount per adjusted trial balance example purpose preparation errors next step unit of product, per unit of input, or per unit of output. A standard is a benchmark that is established to form the basis for cost variance analysis.
A budget expresses management’s plans, while a standard reflects what actually happened. Rather than using a budget at all, consider revising a high-level forecast at frequent intervals. Doing so requires little labor, and more accurately reflects short-term expectations. The flex budget alters expense levels automatically, depending upon the actual revenues achieved. On the contrary, Budgetary Control, as the name suggest, refers to the creation of budgets, then comparing the actual output with the budgeted one and taking corrective action immediately.
Вы должны быть авторизованы, чтобы оставить комментарий.



Об авторе